0x12…qrst

As billion-dollar crypto heists like the ByBit and Infini breaches send shockwaves through the industry, a stark warning is echoing: crypto digital identity security is now the weakest link, the very keys to the kingdom that sophisticated attackers and even rogue insiders are ruthlessly exploiting. This isn’t just about lost funds; it’s about the urgent, fundamental need to secure these diverse digital identities before trust in the entire ecosystem crumbles.
A former developer walks away with around $49.5 million from Hong Kong’s Infini neobank after allegedly exploiting administrative access. At the same time, the largest crypto heist in history unfolds as $1.4 billion in Ethereum vanishes from the exchange ByBit, allegedly linked to the notorious Lazarus Group.
These breaches aren’t just criminal acts but are a stark warning that digital identities — the keys to the crypto kingdom — are the industry’s most vulnerable point.
The ByBit hack, which led to the theft of approximately $1.4 billion in ETH, is a direct blow to trust in cryptocurrency exchanges. According to blockchain analytics firms such as Sayfer, Elliptic, and TRM Labs, the attack has been traced back to the North Korean hacking group Lazarus Group. The stolen funds were tracked to wallets previously associated with hacks against other exchanges like Phemex and BingX.
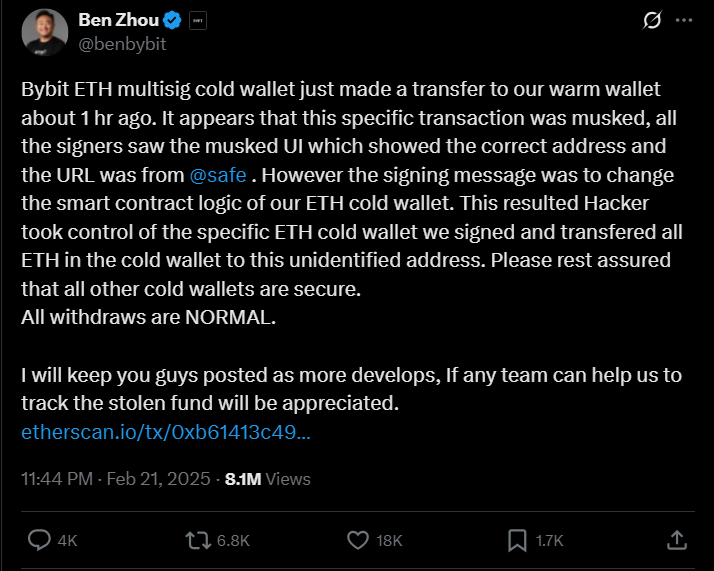
While ByBit has not confirmed the involvement of Lazarus, the mounting evidence points to a well-orchestrated breach. The scale of the theft and the sophisticated laundering of funds suggest that high-level access credentials were likely compromised. While the exact method of the hack remains unclear, the attack underscores how crucial the management of access control is for cryptocurrency exchanges.
Infini, though smaller in scale, presents a disturbing example of insider threats. A former developer, who allegedly retained administrative privileges even after leaving the company, managed to steal $49.5 million in USDC. The funds were converted into DAI, then Ethereum, before being moved to an external wallet.
Unlike the ByBit attack, which involved external hackers, the Infini breach was enabled by a basic failure in managing access rights. The insider’s ability to bypass security measures demonstrates the critical importance of enforcing strict protocols for access control and identity management. Despite the breach, Infini has pledged to reimburse all affected users, offering some reassurance amidst the chaos.

Digital identity in the world of cryptocurrency is far more intricate than simple usernames and passwords. It encompasses a wide range of entities — each holding varying levels of access. These identities are not just limited to individual users but extend to employees, applications, devices, and even decentralized systems.
With so many potential entry points for attackers, understanding the diverse faces of digital identity is crucial to managing security in the crypto space. Each type of identity presents its own set of risks, making it all the more important to implement robust protection measures at every level.

The variety of digital identities in the crypto world introduces numerous opportunities for malicious actors to exploit vulnerabilities. Common tactics used by attackers include:

Given the complex and evolving nature of digital identity, securing it requires a multi-layered approach. Key strategies for safeguarding identities in the crypto space include:

The future of digital identity in crypto is likely to be shaped by greater decentralization, stronger user control, and advanced security measures. New pieces of technology promised to enhance security. Decentralized Identifiers (DIDs), in particular, offer the promise of giving users more control over their identity, reducing reliance on centralized systems.
However, these advancements come with their own set of challenges. Balancing security with usability remains a key concern. Passwordless authentication, for example, could offer strong protection but may also create new complexities for users. Ensuring that new identity systems are scalable, user-friendly, and secure will be essential for their successful integration into the broader crypto ecosystem.
The hacks at ByBit and Infini serve as stark reminders of the vital role digital identity plays in the security of the cryptocurrency world. Each stolen password, compromised API key, or overlooked access privilege can serve as a gateway for attackers. The involvement of a state-sponsored hacking group like Lazarus highlights the increasing sophistication of threats targeting the crypto space.
To build a secure, trustworthy ecosystem, cryptocurrency platforms must rethink how they manage digital identities. Security cannot be an afterthought. It must be the foundation of the entire infrastructure, guiding every decision from platform development to user interaction. Only then can the future of digital finance remain secure.